Electronic & Engineering Materials
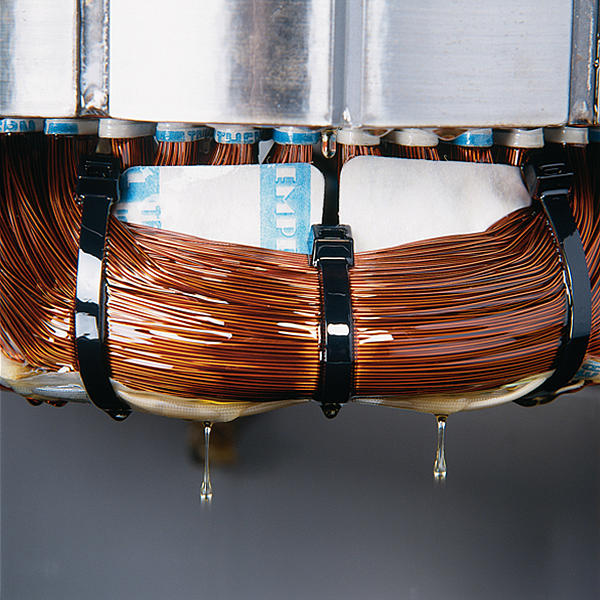
The primary and secondary insulation completes the basic insulation of electrical equipment. For a range of electrical equipments as sensors, instrument transformers, induction systems, and printed wiring boards, additional properties are desired such as improved heat dissipation, much greater mechanical stability at high vibrational forces, noise reduction, and often the complete exclusion of environmental influences.
These properties are obtained
by embedding or completely encapsulating or coating with an insulating material – in blends with other materials also called compound. Depending on whether – in what is usually a thermally based casting process, i.e. a chemical process under the action of heat – the mold is removed after casting or becomes a permanent element of the cast part, the process is referred to as casting insulation or potting insulation respectively.
In many cases the casting process is carried out under a vacuum
to prevent air pockets. Trapped air bubbles reduce heat dissipation, since air is a good heat insulator, or they give rise to disruptive electrical charges in high-voltage applications, which can destroy the insulation. If the part being cast is fully coated with an insulating material, the process is called encapsulation.
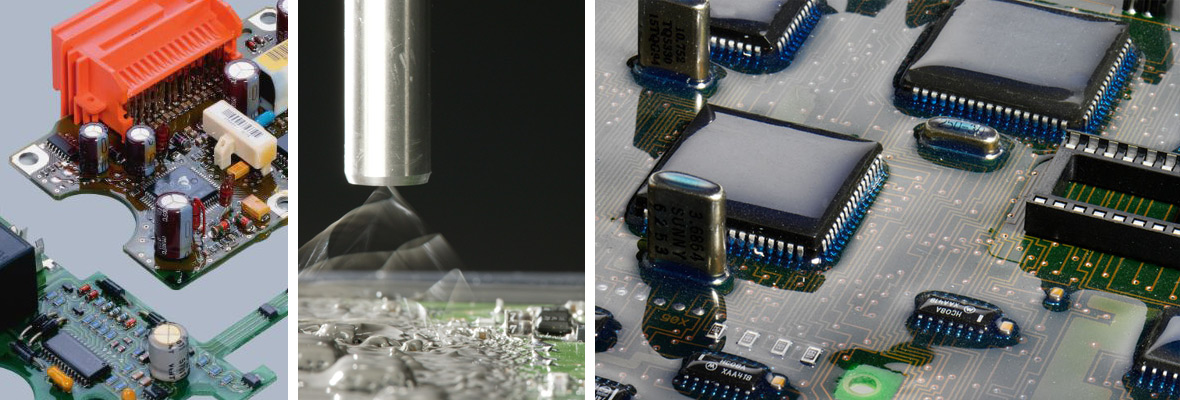
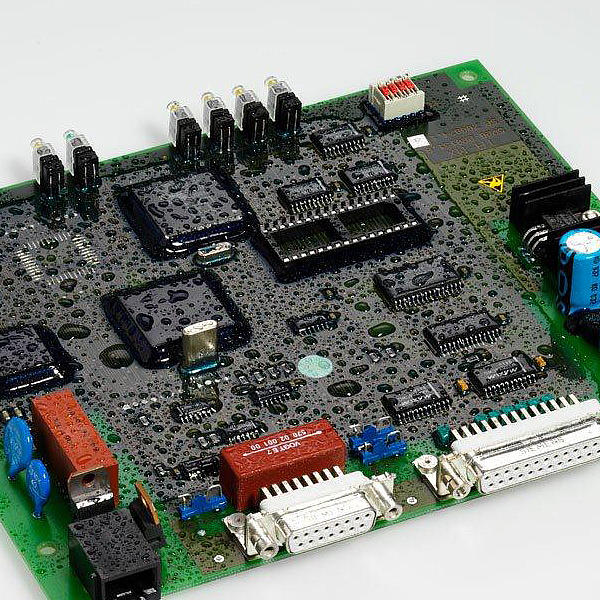
With electronic components, especially printed wiring boards (PWBs), thin layers are applied to protect them from harmful environmental influences. In these cases the process is known as “conformal coating”.
For construction materials
(engineering materials) or engineering workpieces, resins or resin-based compounds are used for electrical and non-electrical applications.
For further improved heat dissipation or mechanical stability, the resin is enriched with inorganic fillers.
The insulating material or construction material consists of organic components (prepolymers) that react to cross-linked polymers during the curing process.
The following different resin systems exist:
- Polyester resins
- Epoxy resins
- Polyurethane resins
- Alkyd resins
- Silicone resins
- Acrylate resins (etc.)